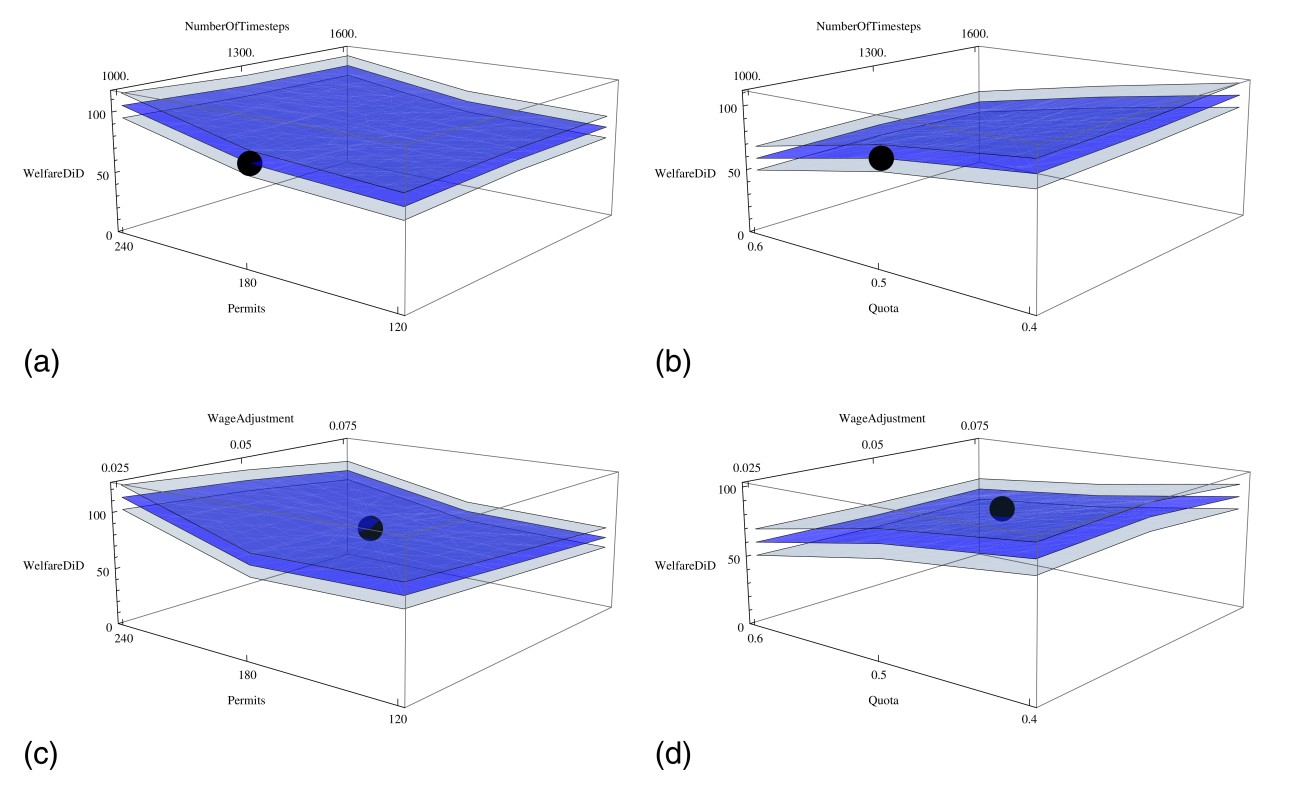
Authors: Michael Neugart and Vahideh Sotoudehmollashahi
Abstract: Water scarcity is a problem likely to become more prevalent in many areas of the world in the near future. Changing water pricing schemes such that households' water demand is reduced could be one policy to address the problem. With water demand of households being price inelastic, such an approach, however, would likely require substantial price increases to reduce water demand. We propose an alternative pricing scheme based on the issuance of water-use rights (permits) to households at prices that cover a water supplier's costs. These permits can be traded at the end of the year, where households in excess of permits are redeemed, and households in need of additional permits have to purchase permits. We show that, in such a setting, opportunity cost considerations of households can curtail water consumption and yield lower water bills than a policy that increases volumetric rates.
Authors: Michael Neugart and Anna Zaharieva
Abstract: Firms organize their production processes differently, with consequences for various metrics of the economy. A so-far little explored issue is whether and how the deepness of firms, meaning the number of hierarchical levels, affects employment segregation in the labor market. We show how the Duncan index, a widely used measure of segregation, changes as firm organizations become deeper, first in a simplified flow model of the labor market, and then when transition probabilities are endogenized in a simulation model with internal promotions and external worker mobility across firms in a frictional environment. Our results suggest that a new hierarchical level can reduce segregation and serve as a stepping stone for disadvantaged workers in the “bottleneck” part of the career ladder. Yet, a new level can turn into a stumbling block for disadvantaged workers increasing segregation, if it is introduced in parts of the career ladder preceding the “bottleneck”.
Authors: Michael Neugart and Vahideh Sotoudehmollashahi
Abstract: One way to address water scarcity could be to change water pricing schemes from flat or uniform rates to block tariffs. Empirical studies evaluating the effect of block rates on water conservation, however, surprisingly yield mixed results. To gain a better understanding of the effects of block pricing on water conservation, we developed an agent-based model of a water market, which we calibrated using data from Germany. Our simulations show that water consumption increases compared to using uniform rates when a decreasing block rate is introduced and decreases when an increasing block rate is introduced. Moreover, block pricing has distributional consequences as measured by households' water bills. We also evaluate the effect of pricing schemes on water consumption and households' water bills under changing price elasticities, a shrinking population, and more hot days.
Authors: Herbert Dawid, Philipp Harting, and Michael Neugart
Abstract: Artificial intelligence algorithms are increasingly used for online pricing and are seen as a major threat to competitive markets. We show that if firms use a deep Q-network (DQN) as an example of a state-of-the-art machine learning algorithm, prices are supra-competitive in duopoly but quickly move to competitive prices as the number of competitors in an oligopoly increases. This finding is very robust concerning variations of the exploration and learning rate used in the DQN algorithm.
Author: Darius Griebenow
Abstract: The EU Emissions Trading System is the cornerstone of Europe's strategy to comply with the Kyoto Protocol and lower its greenhouse gas emissions sufficiently to meet climate goals. Since its implementation in 2005, researchers have sought to not only determine the program's effectiveness in reducing carbon emissions, but also the potentially adverse economic consequences for regulated entities. I study the economic performance of regulated and unregulated firms in Spain, a heavily credit-constrained country whose firms have operated in a deteriorated economic enviroment for a prolonged period of time. Using a difference-in-difference methodological approach, I find regulated Spanish firms benefitted from higher revenues, employment levels, and fixed asset stocks compared to their unregulated counterparts. I also investigate potential channels driving these effects, and find that access to debt is a particularly important factor to consider in the context of Spain. A closer look at the dominant ETS sector in Spain, ceramics and clay production, shows that despite fierce external and internal competition, the sector's ETS firms thrived in particular.
Authors: Darius Griebenow, Michael Neugart, and Stefan Pichler
Abstract: Policies aimed at reducing carbon dioxide emissions are crucial in the fight against climate change. We explore whether political parties that implement environmental regulations face electoral backlash, which could hinder or even obstruct the adoption of climate policies. In particular, using detailed data from the European Union Emissions Trading System, we construct a new index for the stringency of environmental regulation at the regional level (NUTS2) for the European Union. This index is used to assess the economic impact of heightened environmental regulation on regions and to analyze voter reactions to these policies at the polls. Our findings reveal that green parties benefit from stricter environmental regulations in national elections, while this effect is absent in European Parliament elections. The increased vote share for green parties seems to result directly from the regulation rather than being mediated by improvements in regional economic performance.
Authors: Darius Griebenow, Jens J. Krüger, and Michael Neugart
Abstract: When setting up the world's largest emission trading system to reduce carbon dioxide pollution, European policymakers faced intense pressure to supply industry with plenty of emission rights. This has brought attention to the over-allocation of certificates, with limited evidence regarding the extent to which this over-allocation occurred, i.e. that caps were defined too generously. After all, measuring the extent of over-allocation properly requires the construction of a meaningful counter-factual. We propose an approach that exploits a policy change in the allocation of certificates in 2013, when the third phase of the European Emissions Trading System (ETS) started. From then onward, electricity producers were no longer granted free allocations, in contrast to all other installations endowed with certificates. By comparing these groups, we assess how installations would have behaved in Phase 3, had they still received freely allocated certificates as the control group did. Compared to Phase 2, electricity producers in Phase 3 held, on average, 424680 fewer certificates, while emissions, sales, and purchases did not change We interpret these findings indicating toward over-allocation. Relative to the number of certificates awarded to the electricity-generating installations in Phase 2, over-allocation amounts to 64%.

Sponsored by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research
Digital Green Tech funding measure – environmental technology meets digitalization. Duration: 9/2023 to 9/2025.
Short summary: Water management in Germany is neither resource-efficient nor does it meet needs as needed: drought leads to supply gaps, operation is not energy-optimal and there are pipe losses. New, flexible, resource-saving (resources: water, energy, money), but also comprehensible operating strategies are necessary. Although data-based methods of artificial intelligence and heuristic approaches hold considerable potential, questions arise immediately regarding the availability of the necessary data as well as the traceability and transparency of the approaches. These are the reason for the approval trap of autonomous systems. However, if market economy mechanisms are used, with adequate market design, the market's inherent resource and allocation efficiency can be used to achieve comprehensible, resource-efficient and needs-based operating strategies.
Project partners: Michael Neugart, Peter Pelz, Rolf Findeisen, Wilo SE, RheinEnergie
Authors: Herbert Dawid, Philipp Harting, and Michael Neugart
Abstract: We study how the use of machine-learning based algorithms for the determination of wage offers affects workers’ wages on online labor platforms. Firms use reinforcement-learning to update posted wages on the platform, and heterogeneous workers send applications based on the posted information. We show that if firms use a deep Q-network (DQN), as an example of a state-of-the-art machine learning algorithm, the emerging wages closely resemble the equilibrium outcome. However, slightly changing the setup of the algorithms can lead to substantial collusion and wages well below the equilibrium level. In particular, we identify a specific property of the algorithms, namely whether experience replay is used, which determines whether collusion occurs or not. Our findings are robust with respect to many features of the model, including the design of the online labor platform.